4 Cognitive Changes Caused By Depression
Depression leads to various changes in the brain, because it affects brain chemistry. Find out more about this topic today.

The consequences of depression are not just purely emotional disorders that affect mood and feelings. This disease also leads to physical impairments that can affect not only mental health, but also the rest of the organism. Learn more about cognitive changes caused by depression today .
It is a common ailment. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 300 million people worldwide are affected.
On average, 800,000 people each year commit suicide caused by depression. It is also the leading cause of death among young people between the ages of 15 and 29.
These are not temporary emotional changes. The effects on the brain are very difficult to control in those affected.
For this reason, it is of the utmost importance to see a specialist doctor who will prescribe the correct treatment if necessary. Depression does not go away on its own because it is not just a momentary sad state of mind.
Anyone who suffers from it absolutely needs professional help!
Cognitive changes due to depression
Cognitive changes in depression have a direct effect on three areas of the brain: the hippocampus, the amygdala, and the prefrontal cortex. We will then go into more detail about these impairments.
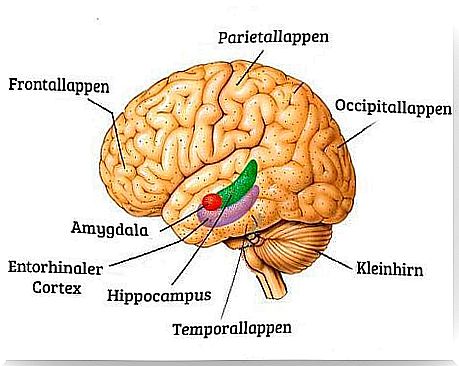
1. Cognitive changes: shrinkage of the hippocampus
The hippocampus is located in the central area of the brain. This brain structure is fundamental to memory and the regulation of cortisol production. This hormone is also known as the stress or happiness hormone.
In the event of physical or mental stress, which can be caused by depression, among other things, the organism releases more cortisol in order to alleviate the consequences of this situation.
But when cortisol levels are high, brain chemistry becomes unbalanced. The formation of neurotransmitters is reduced and the hippocampus can shrink.
2. Cognitive changes: shrinkage of the prefrontal cortex
The frontal brain area or prefrontal cortex is responsible for regulating emotions and memory. This brain structure can also shrink in depression because there is too much cortisol.
The lack of empathy in postpartum depression is believed to be due to this fact.
3. Cognitive changes: swelling of the amygdala
The amygdala is created in pairs and is located in the core area of the brain. Among other things, it is responsible for regulating emotions such as enjoyment, joy or fear.
The excess of cortisol can cause this brain structure to swell. This leads to sleep disorders and changes in normal behavior patterns.
With greater activity, this brain structure also causes more hormones to be released in other parts of the organism than in the normal state, which leads to further health complications.
4. Lack of oxygen supply
In addition to direct cognitive changes caused by depression, other impairments can also indirectly affect the brain. Studies have shown that the body receives less oxygen as a result of the disease.
It is still unclear whether this is due to altered breathing patterns or something else.
It generally affects the cells in the body for which oxygen is essential. In particular, the brain cells suffer from a lack of oxygen supply and can be damaged or die as a result.
Cognitive changes due to depression and its health consequences
Cognitive changes are not immediate, they are the product of a long period of depression. Studies show that the reduction in size of the hippocampus and the prefrontal cortex can be seen after a period of 8 to 10 months.
Dr. Thomas Frodl, who conducts research at the Magedeburg University Hospital, has observed patients with depression for three years to find out how their brain changes physically during this time.

Some of the cognitive consequences of depression include:
- Memory loss
- Decreased neurotransmitter function
- Brain development stagnation
- Decreased ability to learn
- cognitive complaints
- Difficulty concentrating
- Mood swings
- lack of empathy towards others
- Difficulty sleeping
- fatigue
How can cognitive changes due to depression be treated?
Based on the results of various scientific studies, it is believed that the imbalance is caused by an excess of cortisol and other chemicals. This leads to emotional and physical changes in the brain.
For this reason, treatment is attempted to regulate the production of hormones such as cortisol and serotonin. This can be done through inhibitory drugs or therapies.

Psychotherapy is one of the best ways to overcome depression and its health effects. It is important to start doing this immediately after diagnosis.
Researchers confirm that psychotherapy can change brain structure and relieve symptoms of depression. It is therefore important to seek professional help if there is a suspicion of depression.
In addition, other measures are also important to help patients with depression and maintain their brain functions:
- Coping with stress
- Move
- healthy eating
- good sleep
- Avoid alcohol and drugs
Depression is a disorder that goes well beyond mood swings. Although this is not apparent at first glance, the physical changes that affect the wellbeing of those affected are clearly there.