Liver Metabolism: Antibiotics And Alcohol
Both alcohol and antibiotics are toxic substances that are excreted from the body via the liver metabolism. Combining the two can endanger the healthy functioning of the liver.

Have you ever heard that drugs and alcohol should not be combined under any circumstances? When it comes to antibiotics, these precautionary measures must be observed particularly strictly. The reason for this is that the mixture of alcohol and antibiotics has a very negative effect on liver metabolism .
To understand why this is happening, in today’s article we’ll start by explaining certain concepts in more detail. Read on to find out more about this topic!
What is an antibiotic
An antibiotic is a metabolic product of living organisms such as bacteria or fungi, or a synthetic derivative that kills certain sensitive microorganisms or prevents their growth. These drugs are widely used for bacterial infections and are therefore also known as antibacterial drugs.
Generally, antibiotics help a patient’s defense mechanism until the local response is sufficient to control the infection. These medicines act bacteriostatically by preventing the bacteria from growing. If they have a bactericidal effect, they destroy the pathogens. But depending on the drug, both effects can be achieved at the same time.
What is alcohol
Alcohol is a downer that affects the central nervous system and progressively inhibits brain functions. Symptoms of poisoning, which impair gerhin activity, trigger motor coordination problems and behavioral changes, are typical.
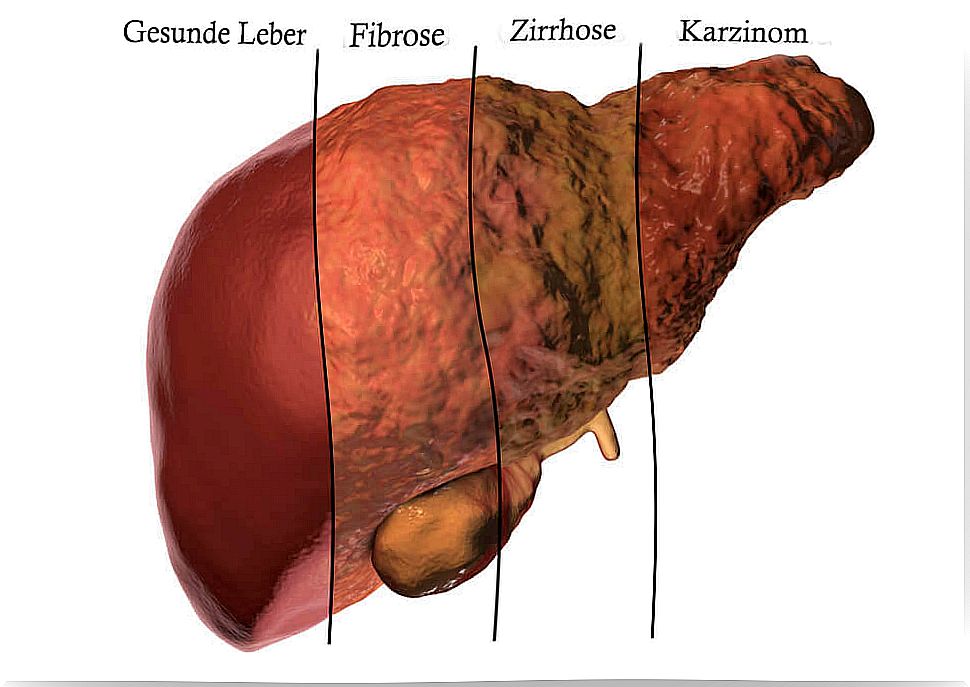
Chronic consumption of alcohol leads to inflammation and the destruction of liver cells. As a result, the disease cirrhosis develops.
What are the functions of the liver? How does liver metabolism work?
The liver is one of the most important organs in the body. In particular, this is due to the fact that it continuously performs numerous basic functions.
These functions include an important role in metabolism, the control of proteins in the blood, and the distribution of certain nutrients such as iron. In addition, the liver regulates the levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood and enables the elimination of toxins.
One of the most important jobs of the liver is to remove toxic substances from the body. Since antibiotics and alcohol are both toxins for the body, the liver is responsible for their metabolism.
However, when too many toxins accumulate in this organ, we speak of toxic hepatitis. Various liver function tests can be performed to find out whether the liver metabolism is working properly. These analyzes are important to assess liver activity.
Liver metabolism and liver function tests
Various liver function tests can be used to assess the functionality of this organ by measuring certain proteins, enzymes and substances:
- Bilirubin : This yellowish substance is produced when the red blood pigment is broken down. Tests can be used to determine the levels of bilirubin in the urine or blood. If the bilirubin levels in the blood are too high, jaundice (jaundice) develops.
- Aminotransferases: These enzymes provide information about the integrity of the hepatocytes (liver cells). The values are increased, for example, in hepatocellular necrosis (ie when the liver cells die).
- Alkaline phosphatase (AP): The most sensitive marker is cholestasis, even if it is not specific to just one disease.
Liver metabolism and toxic hepatitis
Toxic hepatitis is inflammation of the liver. The causes for this can be very different, the most common being an infection. But there are other reasons as well, such as an abnormal response to a drug or exposure to toxins in nature.
In addition to the triggers mentioned , toxic hepatitis can result from the combined use of antibiotics and alcohol. This is due to the fact that these two active substances influence each other. If this is the case, two mechanisms can be distinguished:
- Direct or intrinsic toxic effects: Both alcohol and antibiotics are toxins that are metabolized in the liver. If the liver metabolism is overloaded, it cannot function properly and hepatitis develops as a result.
- Idiosyncratic toxic effect: certain antibiotics interact with alcohol and become inactive. This makes them ineffective and can no longer kill bacteria. The big problem in this case is that the bacteria that should have been fought become resistant to the antibiotic used. Therefore, it is then much more complicated to take action against the causative bacteria.
To illustrate idiosyncratic toxic hepatitis, we can mention the antibiotic amoxicillin / clavulanic acid. Currently, this drug is the leading cause of idiosyncratic toxic hepatitis in western countries. When combined with alcohol, this drug becomes ineffective and leads to bacteria resistance. The bacteria can therefore no longer be fought with this antibiotic.
The risk of bacterial resistance
The resistance that bacteria develop to antibiotics is always greater. This also increases a serious problem of the general health of the world’s population. In order to prevent resistance, it is essential to only take antibiotics according to your doctor’s prescription and instructions.
Under no circumstances should self-treatment with these drugs take place in order to combat viral diseases such as flu or colds. It is also important to avoid the combined intake of antibiotics and alcohol or other dangerous substances.