Gluten Intolerance: The Diagnosis Of Celiac Disease
Gluten intolerance is a chronic disease that is characterized by insufficient nutrient absorption as the mucous membrane of the small intestine is damaged. However, if a doctor makes the correct diagnosis, the patient can avoid many of the symptoms and complications of the disease.

Celiac disease is a form of gluten intolerance and describes chronic hypersensitivity to a protein found in some foods, such as cereals. Experts estimate that it affects around 1% of the population and is more common in women than men.
This type of gluten intolerance occurs in people who have genes that make them susceptible to celiac disease . It is characterized by an immune-based inflammatory reaction in the mucous membrane of the small intestine. This in turn affects the absorption of macro and micronutrients.
As we mentioned earlier, it is a chronic autoimmune disease. This means that the immune system itself attacks cells as a form of protection.
Gluten intolerance in the form of celiac disease
What is the cause of the manifestation of gluten intolerance?

No single cause is responsible for the development of gluten intolerance. Rather, it is a combination of factors that make intolerance appear.
Genetic predisposition, certain structural abnormalities in the small intestine, and a diet containing gluten are examples of predisposing factors for the development of gluten intolerance.
For all of these reasons, we can say that it is a bowel disease that manifests itself in genetically susceptible people. These people are unable to digest a protein found in gluten called gliadin.
So when these people eat foods that contain gluten, their small intestines react and become inflamed. When this happens, the intestines have difficulty absorbing the nutrients from the food.
Gluten intolerance: the diagnosis of celiac disease
It is not easy to diagnose gluten intolerance. This is because, until recently, it was only diagnosed if there were clear clinical symptoms. In addition, this disease has a wide variety of symptoms that can be traced back to other diseases.
However, even if there are no symptoms, some experts believe that it is possible to detect the disease if it is suspected. This can be done either by intolerant relatives or for other reasons. For this reason, doctors request serologies, genetic tests, or a histology.
On the other hand, medical professionals can currently also request clinical diagnostic tests, such as a blood test that contains the serological markers for celiac disease. These markers are antibodies such as:
- Anti-gliadin
- Anti-tissue transglutaminase
- Anti-endomysial
Symptoms of Celiac Disease
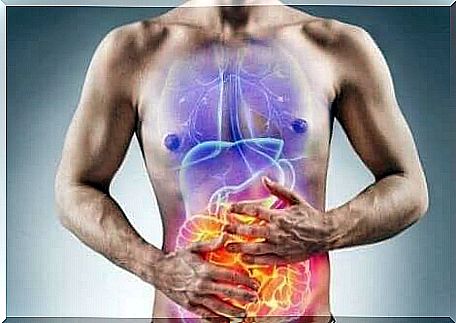
When a person who does not tolerate gluten ingests foods that contain gluten, it triggers an autoimmune reaction that causes inflammation and deterioration of the lining of the small intestine. The following symptoms, among others, usually occur:
- nausea
- Vomit
- diarrhea
- Light weight
- Growth problems
In adults, on the other hand, most cases manifest themselves with discrete symptoms. Symptoms include mild diarrhea, weight loss, anemia, and constipation 10% of the time.
Since the small intestine is unable to absorb the necessary nutrients, there is insufficient nutrient absorption through the intestine. Because of this, you may experience other symptoms such as bruising or nosebleeds.
In turn, it is normal for the patient to feel tired or have itchy skin and eventually develop dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) and even hair loss.
Mouth ulcers also occur and women often suffer from missed menstrual periods. However, muscle cramps or intolerance to other nutrients, such as lactose, are also common.
Can someone have Asymptomatic Celiac Disease?
Keep in mind that not all gluten intolerant patients will experience the above symptoms as some are asymptomatic.
If so, you may be wondering how it is possible that they can be diagnosed with the disease if they don’t have symptoms.
The explanation for this is that gluten intolerance in the form of celiac disease is a disease with a genetic predisposition. In order for a doctor to make a diagnosis, as mentioned above, they must request a blood test with the disease markers. However, after a biopsy, deterioration of the bowel can be observed.
In short, even if a patient does not have the most obvious symptoms, such as vomiting or diarrhea, the lining of the intestines can still be affected. This can lead to other illnesses or complications for the patient if he does not adhere to proper diet.