Inflammation Of The Esophagus: Symptoms And Treatment
Inflammation of the esophagus is usually chronic but can be treated well. The symptoms vary in intensity and usually come on in bursts.

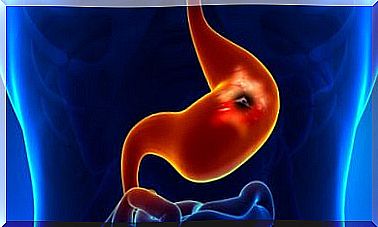
In technical jargon , the inflammation of the esophagus is also known as reflux esophagitis or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The gastric juice flows back into the esophagus and leads to erosive damage to the esophageal mucosa, although there is usually no specific trigger for this.
The cause of the reflux into the esophagus is often the temporary and spontaneous relaxation of the lower esophageal tendon (LES), which is located between the stomach and esophagus. This sphincter muscle is responsible for opening when swallowing to let the food pass through, but then preventing stomach acid or food from getting back up the esophagus.
The inflammation of the esophagus affects the quality of life of people affected. However, this condition is only diagnosed as a disease if the symptoms are significant or intense and have been present for an extended period of time.
Reflux esophagitis is generally chronic, but the prognosis is usually good. The symptoms show up in varying degrees of intensity and usually appear in bursts.
Causes of inflammation of the esophagus
With an inflamed esophagus there are various factors that need to be considered. As already mentioned, the lower esophageal pain usually does not work properly. In addition, other conditions promote the reflux of stomach acid and chyme into the esophagus:
- Reduced mobility of the esophagus, which means that the esophagus cannot clean itself properly
- Relaxation of the upper esophageal sphincter
- In many cases, reflux disease also arises as a complication of a hiatal hernia.
Inflammation of the esophagus: symptoms
Reflux esophagitis manifests itself through a wide variety of symptoms. In addition, different degrees of severity are distinguished (stages I, II, III and IV). In some cases, there may be additional complications, as the inflammation triggers a stenosis, ulcers in the esophagus or a chronic inflammatory change in the esophagus (Barrett’s esophagus).
The symptoms depend, among other things, on the duration of the relapses, the intensity, the type and the volume of the reflux. In addition, the time at which the stomach acid comes into contact with the mucous membrane of the esophagus is crucial.
Common symptoms are:
- Heartburn is one of the most common signs of an inflamed esophagus. This leads to an uncomfortable burning sensation in the esophagus.
- Acid regurgitation is also a common symptom. In this case, the stomach contents spontaneously reach the mouth via the esophagus. The risk of this is increased when lying down or when pressure is applied to the abdomen.
- Chest pain that is acute and sudden and caused by cramps in the esophagus. This pain is mostly due to GERD when it is related to food ingestion rather than exertion.
- Dysphagia or odynophagia (difficulty swallowing). Odynophagia is a rare symptom of reflux oesophagitis, but it can indicate this problem.
Typical symptoms of GERD enable a reliable diagnosis. If the symptoms mentioned are present, the doctor can usually make the diagnosis without further examinations (such as with an endoscope) and initiate the appropriate treatment.
However, if alarming symptoms are present or if conventional treatment is unsuccessful, further upper digestive tract examinations with an endoscope are required.
Inflammation of the esophagus: treatment options
Treatment for an inflamed esophagus is aimed at relieving symptoms and inflammation. It is also intended to prevent further complications. Furthermore, precautionary measures are important to avoid future discomfort.
With this in mind, proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle are of great importance. In addition, certain hygiene measures must be taken into account. In many cases, drug therapy is used, but surgical intervention is sometimes required.
Hygiene and nutritional habits in the prevention and treatment of inflammation of the esophagus

The recommendations regarding lifestyle, hygiene and eating habits must be made individually, because different risk factors play a role in each patient. In addition, the clinical response to the changes introduced must be taken into account.
In any case, it is advisable to quit smoking and reduce alcohol consumption as much as possible. Additionally, obese people should try to lose weight to better control the problem.
In addition, it is usually worth raising the head of the bed slightly if you experience discomfort while you are sleeping.
The following general recommendations are also helpful:
- Avoid large meals. It is better to eat smaller portions, but take something more often during the day.
- Observe which foods trigger symptoms and avoid them.
- Try to control stress.
- You shouldn’t do too much physical exertion.
- Take the time to chew the food well.
Inflammation of the esophagus: drug treatment
The pharmacological treatment is carried out by inhibiting or neutralizing the acidic gastric juices. For example, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are used for this. These also relieve symptoms, promote wound healing in the esophagus, and help prevent relapses.
In addition, antacids are used to reduce stomach acid and provide quick relief from heartburn. Prokinetic drugs are very useful when regurgitation is a major symptom. Anti-H2 agents partially inhibit the production of stomach acid and are used in cases of reflux when there is no inflammation of the esophagus.
Are you affected by this disease? In this case, seek thorough advice from your doctor and try to control the causal factors as well as possible in order to alleviate the symptoms. Your doctor will prescribe the best treatment for you individually.